Pneumatic systems play an important role in various industries, offering versatile, reliable, and cost-effective solutions for automation and control. These systems utilize compressed air to power a range of mechanical processes, ensuring high efficiency and precision. Their application spans across numerous sectors, from automotive manufacturing to food processing, highlighting their importance in modern industrial operations.
Pneumatic systems are extensively used in industries for tasks such as material handling, assembly, packaging, and automation. They provide high force, speed, and accuracy, making them essential for applications that require precise control and reliable performance.
Understanding the specific applications of pneumatic systems in different industries highlights their indispensable role in modern manufacturing and automation.
Detailed Applications of Pneumatic Systems in Industry
Material Handling

Using pneumatic conveying equipment in manufacturing
Resource: https://www.designworldonline.com
Conveyor Systems: Pneumatic cylinders are used to move products along conveyor belts in manufacturing and packaging plants. They provide the necessary push or pull force to transport items efficiently. For example, in a bottling plant, pneumatic cylinders can control the flow of bottles on the conveyor, ensuring smooth and continuous movement without jams.
Pick and Place Systems: Pneumatic actuators enable robotic arms to pick up objects from one location and place them in another with high precision and repeatability. In electronic assembly lines, for instance, pneumatic pick and place machines can handle delicate components without causing damage, significantly improving production speed and accuracy.
Assembly Processes
Pressing and Clamping: Pneumatic cylinders are used in assembly lines to press parts together or clamp components in place during manufacturing. This ensures secure and accurate assembly of products. In the automotive industry, pneumatic clamps are used to hold car parts together during welding processes, ensuring precise alignment and strong welds.
Fastening: Pneumatic tools, such as nail guns and screwdrivers, are used to fasten components quickly and consistently, improving assembly speed and quality. In furniture manufacturing, pneumatic nail guns are essential for quickly and securely assembling wooden frames, significantly reducing production time compared to manual nailing.
Packaging
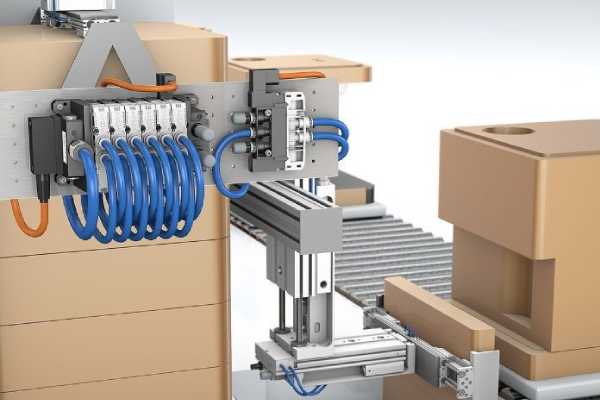

Filling and Sealing: Pneumatic systems control the filling of containers with liquids, powders, or granules and ensure airtight sealing, essential for maintaining product quality and safety. In the pharmaceutical industry, pneumatic filling machines are used to dispense precise amounts of liquid medication into bottles, followed by sealing caps to ensure sterility and prevent contamination.
Labeling and Sorting: Pneumatic cylinders help in the accurate placement of labels on products and sorting items into categories, enhancing packaging efficiency. For example, in a dairy processing plant, pneumatic systems can control labeling machines that apply labels to milk cartons accurately, ensuring proper branding and information display.
Automation
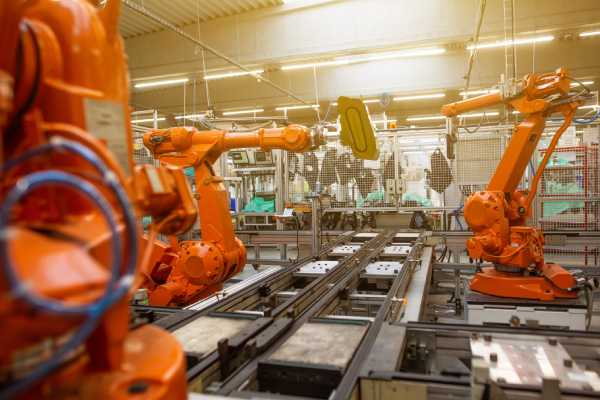

Robotic Systems: Pneumatic actuators drive the movement of robotic arms and grippers in automated systems, providing precise control for tasks such as welding, painting, and inspection. In automotive manufacturing, robotic arms equipped with pneumatic actuators can perform spot welding with high precision and speed, improving production efficiency and product quality.
Actuation of Valves and Gates: Pneumatic systems control the opening and closing of valves and gates in various industrial processes, ensuring smooth and reliable operation. In the oil and gas industry, pneumatic actuators are used to control the flow of fluids through pipelines by opening and closing valves based on process requirements.
Automotive Industry

Brake Systems: Pneumatic brake systems are used in commercial vehicles to provide reliable stopping power. Compressed air is used to activate the brake mechanisms, ensuring safety and efficiency. For example, large trucks and buses use pneumatic brakes because of their ability to provide strong and consistent braking force, essential for stopping heavy loads safely.
Suspension Systems: Pneumatic suspensions provide adjustable ride height and improved comfort in vehicles by using air springs controlled by pneumatic valves. In luxury cars, pneumatic suspension systems can automatically adjust the ride height based on driving conditions, providing a smoother and more comfortable ride.
Pharmaceutical and Food Industries
Cleanroom Applications: Pneumatic systems are preferred in cleanroom environments due to their cleanliness and minimal risk of contamination. They are used in automated machinery for filling, sealing, and packaging medications and food products. In a pharmaceutical cleanroom, pneumatic systems ensure that tablets are precisely filled into blister packs without introducing contaminants.
Dispensing Systems: Pneumatic systems control the precise dispensing of liquids and powders, ensuring accurate dosing and consistency in product formulation. In the food industry, pneumatic dispensers can accurately portion out ingredients such as sauces or powders onto assembly lines, maintaining consistent product quality.
Advantages of Using Pneumatic Systems in Industry
Pneumatic systems offer numerous benefits, including:
- High Speed and Force: Pneumatic actuators provide rapid movement and high force output, making them suitable for demanding applications.
- Reliability: Pneumatic systems are robust and can operate in harsh environments where electrical systems may fail.
- Safety: Using air as a power source reduces the risk of fire and electrical hazards, enhancing workplace safety.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Pneumatic components are generally less expensive and easier to maintain than hydraulic or electric systems.
Challenges in Implementing Pneumatic Systems
Despite their advantages, pneumatic systems face challenges such as air leakage, pressure drops, and the need for regular maintenance. Proper installation, regular inspection, and advancements in sealing technologies can help mitigate these issues. For instance, using high-quality seals and fittings can reduce air leakage, while regular maintenance can ensure optimal system performance.
Future Trends in Pneumatic Technology
Innovations in pneumatic technology, such as smart sensors and advanced materials, are set to enhance the performance and efficiency of pneumatic systems, driving further advancements in industrial automation. Smart sensors can monitor cylinder performance in real-time, providing data on parameters such as position, speed, and force. This information can be used to optimize operations, predict maintenance needs, and reduce downtime. Advanced materials are also being developed to improve the durability and efficiency of pneumatic cylinders, making them more suitable for harsh environments and demanding applications.
Summary
In conclusion, pneumatic systems are indispensable in various industries, providing high efficiency, precision, and reliability. By understanding their specific applications and benefits, industry professionals can optimize their use in manufacturing and automation processes, ensuring continued productivity and innovation. As technology advances, pneumatic systems will continue to play a crucial role in the evolution of industrial automation, driving efficiency, precision, and cost-effectiveness in manufacturing processes.