If you’re new to buying air filters for pneumatic systems, you might have come across terms like NPT and BSP. Understanding these two types of thread standards can be a bit confusing at first, but choosing the right one is crucial for the performance and reliability of your system.
In this beginner’s guide, we’ll break down what NPT and BSP air filters are, how they differ, and the key factors you need to consider before making a purchase. By the end, you’ll have the knowledge you need to confidently choose the best air filter for your needs.
What is an Air Filter in a Pneumatic System?
Before we dive into NPT and BSP, let’s quickly talk about what an air filter does. In a pneumatic system, an air filter is used to remove unwanted particles, dust, water, and oil from the compressed air supply. Clean air is essential to keep the system running smoothly and prevent damage to your equipment.
Understanding NPT and BSP Threads
NPT and BSP are two different standards for screw threads used to connect pipes and fittings. They determine how the parts fit together, how tight the seal is, and whether or not the connection will leak. Let’s take a closer look at each:
1. What is an NPT Air Filter?
NPT stands for National Pipe Thread, a standard commonly used in the United States and Canada. NPT threads are tapered, meaning they get narrower as they go further into the connection. This design helps create a tight seal that prevents air leaks.
Key Features of NPT Air Filters:
- Tapered Threads: Tapered threads mean the diameter gets smaller, creating a wedge-like effect that seals tightly.
- Angle: The thread angle for NPT threads is 60 degrees, which contributes to the sealing effect.
- Location: Most commonly used in the USA, Canada, and regions that follow American standards.
- Sealant Requirement: NPT threads usually need a sealant like PTFE tape or pipe dope to ensure a leak-proof connection.
2. What is a BSP Air Filter?
BSP stands for British Standard Pipe, a thread standard commonly used in the UK, Europe, Asia, and other parts of the world. BSP threads can be either parallel (BSPP) or tapered (BSPT).
- BSPP (Parallel): The threads have a constant diameter, meaning they do not taper.
- BSPT (Tapered): Similar to NPT, these threads get narrower to create a tighter fit.
Key Features of BSP Air Filters:
- Thread Types: BSPP (parallel) and BSPT (tapered) come in two types.
- Angle: The thread angle for BSP threads is 55 degrees.
- Location: Commonly used in Europe, Asia, and regions that follow British standards.
- Sealing Method: Often uses a gasket or O-ring to ensure a tight, leak-proof connection.
NPT vs. BSP: A Simple Comparison for New Buyers
| Feature | NPT Air Filter | BSP Air Filter |
|---|---|---|
| Thread Type | Tapered (NPT) | Parallel (BSPP) and Tapered (BSPT) |
| Thread Angle | 60 degrees | 55 degrees |
| Primary Use | North America | UK, Europe, Asia, and other regions |
| Sealing Requirement | Requires thread sealant (e.g., PTFE tape) | Often uses O-rings or gaskets for sealing |
| Compatibility | Best for American-standard systems | Best for British and European systems |
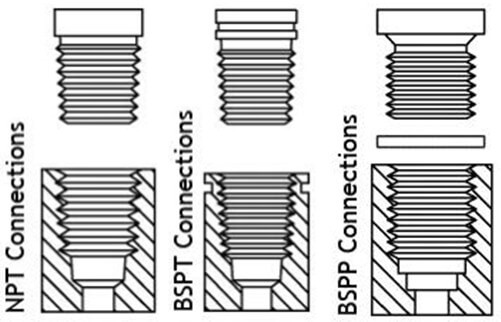
How to Tell the Difference Between NPT and BSP Threads
As a newbie buyer, you might wonder how to tell NPT and BSP threads apart when looking at them:
- Check the Thread Angle: NPT threads have a 60-degree angle, while BSP threads have a 55-degree angle.
- Look for Tapering: Both NPT and BSPT threads are tapered, but BSPP threads are parallel. If the threads maintain the same diameter all the way, it’s likely BSPP.
- Labeling: Manufacturers often label the threading standard on the filter or its packaging. Look for markings like “NPT,” “BSPP,” or “BSPT.”
Advantages of NPT Air Filters
- Strong Sealing Power: NPT’s tapered threads create a reliable and durable seal when used with a thread sealant.
- Widely Available in North America: If you’re in the USA or Canada, NPT filters are easy to find and compatible with most local systems.
- Ideal for High Pressure: NPT threads are excellent for high-pressure environments because of their secure sealing design.
Advantages of BSP Air Filters
- Global Compatibility: BSP threads are widely accepted across the UK, Europe, and Asia, making them ideal for international use.
- Flexible Options: The availability of both BSPP (parallel) and BSPT (tapered) threads gives you more versatility for different setups.
- Effective Sealing with O-Rings: The use of O-rings or gaskets with BSP filters often provides a better seal, especially in lower-pressure systems.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Choosing NPT or BSP Air Filters
- Mixing NPT and BSP Threads: Never mix NPT and BSP threads as they are not designed to work together. This mismatch can lead to poor connections and leaks.
- Skipping the Sealant: If you’re using NPT filters, always remember to apply a sealant like PTFE tape to prevent leaks.
- Ignoring Compatibility: Before purchasing, double-check that the air filter’s thread type matches the other components of your pneumatic system.
How to Choose the Right Air Filter for Your System
- Identify the Standard: Know which standard your system uses — NPT for American systems or BSP for European and Asian systems.
- Consider the Environment: Choose NPT for high-pressure systems due to its strong seal, and consider BSP if you’re using O-rings for better flexibility.
- Check Availability: If you’re in a specific region, buy the air filter that matches the most common thread type in that area for easier replacements.
Conclusion
Choosing between NPT and BSP air filters doesn’t have to be overwhelming, even if you’re a beginner. The main thing to remember is that NPT is best suited for systems in North America, while BSP is commonly used internationally. Understanding the differences in their thread designs and sealing methods will help you make the right choice and ensure that your pneumatic system runs efficiently without leaks.
If you’re still unsure about which air filter is right for your needs, feel free to reach out to our experts. We’re here to help you make the best choice for your pneumatic system!