Are you curious about how certain machines achieve precise and powerful movements in both directions? The answer often lies in double-acting pneumatic cylinders, crucial components in various industrial applications. By understanding these cylinders, you can gain valuable insights into the mechanisms that drive modern machinery.

A double-acting pneumatic cylinder is a type of cylinder where the output force or thrust generated by the piston moves in both forward and retracting directions. It uses two ports to operate and is commonly referred to as an “air” cylinder.
Understanding these cylinders can unlock insights into modern machinery’s efficiency and versatility. Let’s dive deeper into their structure, working principles, types, applications, and benefits.
What is a Double Acting Pneumatic Cylinder?
A double-acting pneumatic cylinder, also known as an air cylinder, utilizes compressed air to produce linear motion. Unlike single-acting cylinders, which use air pressure to move the piston in one direction and rely on a spring to return it, double-acting cylinders apply air pressure to both sides of the piston, allowing it to move back and forth with equal force. This bidirectional movement is essential in applications requiring precise control and force in both directions.
Detailed Working Principles of Double-Acting Pneumatic Cylinders
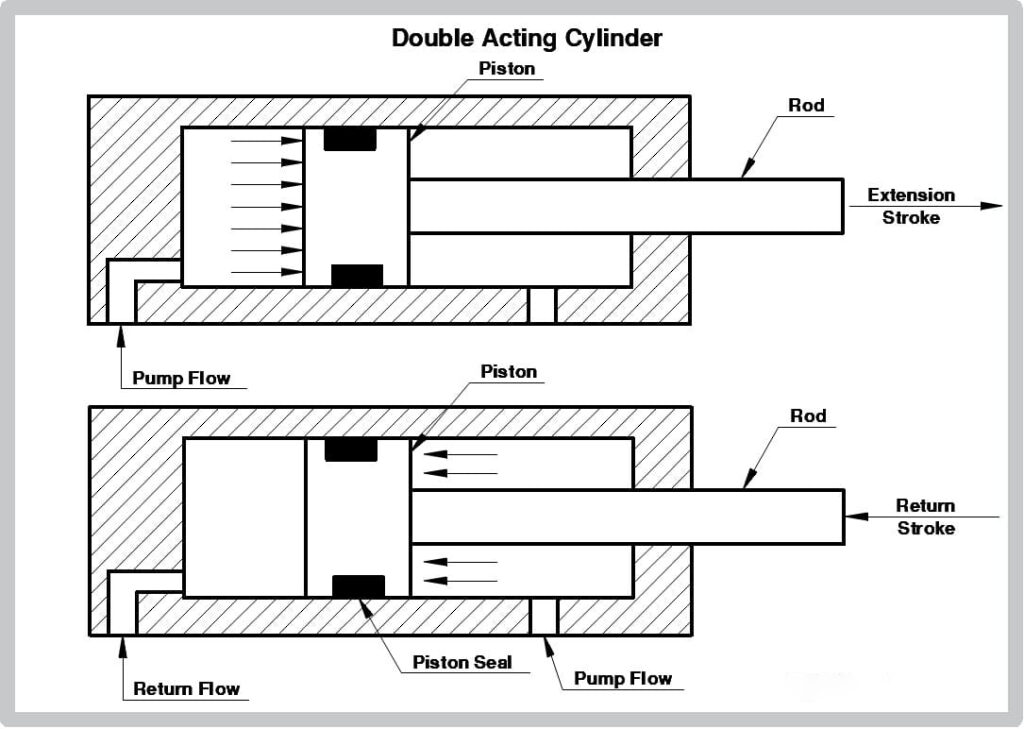
Double-acting pneumatic cylinders function by alternating the application of air pressure to either side of a piston within a cylinder. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of the working principles:
- Air Ports: The cylinder has two air ports, one at each end. These ports allow compressed air to enter and exit the cylinder. When air pressure is applied to one port, it pushes the piston towards the opposite end.
- Piston Movement: The piston inside the cylinder is moved by the air pressure applied to the ports. When air is supplied to the port at one end, it creates pressure against the piston, pushing it to the opposite end. This movement can perform various tasks, such as pushing a load or extending an arm.
- Reversal: When the air supply to the initial port is cut off and redirected to the port at the opposite end, the air pressure moves the piston back to its original position. This retracting motion is as powerful as the extending motion, thanks to the equal application of air pressure.
- Control Systems: Modern pneumatic systems often incorporate sophisticated control systems that precisely regulate the air pressure and flow to the cylinder. This allows for fine-tuned control of the piston’s movement, making double-acting cylinders ideal for applications requiring high precision.
This bidirectional control allows for precise and powerful movements essential in various mechanical applications.
Types of Double-Acting Pneumatic Cylinders
Double-acting pneumatic cylinders come in several types, each suited for specific applications:
- Standard Cylinders: These are general-purpose cylinders used in a wide range of applications, from simple automation tasks to complex machinery operations.
- Compact Cylinders: Designed for applications where space is limited, compact cylinders offer the same functionality as standard cylinders but in a smaller package. They are ideal for use in tight spaces or where the equipment size is a constraint.
- Rodless Cylinders: Ideal for long-stroke applications, rodless cylinders have the piston connected internally, eliminating the need for an extended rod. This design is beneficial in applications requiring long linear movement without increasing the overall length of the cylinder.
- Tandem Cylinders: Featuring two cylinders combined in line to provide increased force, tandem cylinders are used in applications where a single cylinder’s force is insufficient. By combining two cylinders, they can deliver significantly more power without needing a larger bore size.
- Rotary Cylinders: These cylinders convert linear motion into rotational motion, making them suitable for applications requiring rotation, such as turning valves or positioning mechanisms.
- Double-Rod Cylinders: These cylinders have rods extending from both ends of the piston, providing balanced force and movement. They are commonly used in applications where equal force is required in both directions.
Applications of Double Acting Pneumatic Cylinders
Double-acting pneumatic cylinders are versatile and find use in numerous industries:
- Manufacturing: Used in assembly lines, automated processes, and material handling, double-acting cylinders are essential in manufacturing environments. They perform tasks such as pushing, pulling, lifting, and positioning components with high precision and reliability.
- Automotive: Employed in car manufacturing for tasks such as lifting, pressing, and moving components, these cylinders help automate various processes in the automotive industry. They are used in robotic arms, welding machines, and assembly lines to enhance efficiency and productivity.
- Robotics: Integral to robotic arms and other automated machinery, double-acting pneumatic cylinders provide the precise and controlled movement required in robotics. They enable robots to perform complex tasks such as picking and placing objects, assembling parts, and performing repetitive actions with high accuracy.
- Packaging: Used for operations like sealing, cutting, and boxing, double-acting cylinders ensure that packaging processes are efficient and consistent. They are employed in machines that handle tasks such as filling containers, sealing packages, and cutting materials to specific lengths.
- Agriculture: In agricultural machinery, double-acting cylinders are used for tasks such as controlling the movement of plows, adjusting the height of implements, and operating gates and doors. They help improve the efficiency and effectiveness of various farming operations.
- Aerospace: In the aerospace industry, these cylinders are used in aircraft control systems, landing gear mechanisms, and cargo handling equipment. They provide the precise and reliable movement necessary for critical aerospace applications.
- Medical Equipment: In medical devices and equipment, double-acting pneumatic cylinders are used for applications such as adjusting patient beds, operating surgical instruments, and controlling the movement of diagnostic machines. They ensure smooth and controlled motion, enhancing the functionality of medical equipment.
Benefits of Double Acting Pneumatic Cylinders
There are several advantages to using double-acting pneumatic cylinders:
- Precise Control: Allows for exact positioning and controlled movements in both directions. This precision is essential in applications where accuracy is critical, such as in manufacturing and robotics.
- Efficiency: Faster operation compared to single-acting cylinders due to bidirectional movement. The ability to move the piston in both directions without relying on external forces or springs makes double-acting cylinders more efficient in performing tasks.
- Versatility: Suitable for a wide range of applications, from light-duty tasks to heavy industrial operations. The versatility of these cylinders makes them a valuable component in various industries, from automotive to aerospace.
- Durability: With proper maintenance, they offer long service life and reliable performance. Double-acting cylinders are designed to withstand the rigors of industrial environments, ensuring that they can operate reliably over extended periods.
- Cost-Effective: While the initial cost may be higher than single-acting cylinders, the efficiency and durability of double-acting cylinders often result in lower overall costs due to reduced maintenance and downtime.
Difference Between Single and Double Acting Pneumatic Cylinders
The main differences between single and double acting pneumatic cylinders are:
- Ports: Single-acting cylinders have one air port, while double-acting cylinders have two. The additional port in double-acting cylinders allows for bidirectional movement.
- Movement: Single-acting cylinders move in one direction using air pressure and return via a spring. Double-acting cylinders move in both directions using air pressure, providing force in both the extension and retraction strokes.
- Force: Double-acting cylinders provide force in both directions, making them more suitable for applications requiring constant force. Single-acting cylinders rely on a spring to return the piston, which can limit their force and speed.
- Tillämpningar: Single-acting cylinders are typically used in simpler applications where movement in one direction is sufficient, such as in clamping and lifting tasks. Double-acting cylinders are preferred in applications requiring more complex and precise control, such as in automation and robotics.
Double Acting Pneumatic Cylinder Working Principle
To further understand the working principles, consider a double-acting pneumatic cylinder’s internal mechanism:
- Initial State: Air pressure is applied to one port, moving the piston and performing a task. The piston moves in the direction of the port with the applied air pressure, extending the cylinder.
- Changeover: The control system switches the air supply to the opposite port. This switch is usually controlled by a directional control valve, which directs the flow of air to the appropriate port.
- Retraction: Air pressure on the new port moves the piston back, readying it for the next cycle. The piston moves in the opposite direction, retracting the cylinder and resetting it for the next operation.
Modern pneumatic systems often incorporate sensors and feedback mechanisms to monitor the position and movement of the piston. These systems provide real-time data that can be used to adjust the air pressure and flow, ensuring precise control and operation of the cylinder.
Specifications and Symbols of Double-Acting Pneumatic Cylinders
When selecting a double-acting pneumatic cylinder, consider the following specifications:
- Bore Size: Diameter of the cylinder’s piston. The bore size determines the amount of force the cylinder can generate.
- Stroke Length: Distance the piston travels within the cylinder. The stroke length defines the range of movement the cylinder can achieve.
- Operating Pressure: Maximum and minimum air pressure the cylinder can handle. The operating pressure affects the cylinder’s performance and the force it can exert.
- Mounting Options: Various methods to mount the cylinder in place. Common mounting options include flange mounts, foot mounts, and trunnion mounts.
Symbols used in technical drawings include:
- Arrow Indicators: Show the direction of airflow. Arrows indicate the path of air through the ports and the direction of piston movement.
- Port Labels: Indicate the location of air ports. Labels such as A and B or 1 and 2 are used to differentiate between the ports.
- Piston Rod: Represented by a solid line with arrows showing movement direction. The piston rod symbol indicates the direction in which the piston moves when air is applied.
Cost and Maintenance of Double-Acting Pneumatic Cylinders
Cost considerations include the cylinder’s size, material, and specifications. High-quality materials and precise manufacturing processes can increase the cost but also enhance the performance and durability of the cylinder.
Maintenance tips to ensure longevity:
- Regular Inspection: Check for air leaks and wear. Inspect seals, fittings, and connections to ensure there are no air leaks that can reduce efficiency.
- Lubrication: Keep the cylinder well-lubricated to reduce friction and wear. Proper lubrication ensures smooth operation and extends the life of the cylinder.
- Cleaning: Regularly clean to prevent dust and debris buildup. Cleaning the cylinder and its components prevents contamination that can cause wear and damage.
By following these maintenance practices, you can ensure that your double-acting pneumatic cylinders operate efficiently and have a long service life.
Summary
Double-acting pneumatic cylinders are essential components in modern machinery, offering precise control and efficient operation. Their versatility and robust performance make them indispensable in various industries. Understanding their working principles, types, applications, and benefits can significantly enhance your knowledge of industrial automation and machinery.